The concept behind Xqueeze
How is Xqueeze different?
The primary differences of approach in Xqeeze that allow overcoming of the above mentioned shortcomings are:
- Enabling direct generation of compact XML: Xqueeze enables an XML generator to directly generate "compact XML" (henceforth denoted as xqML). This allows usage in applications where there is streaming XML data generation and consumption.
- No additional overheads: xqML generators need not use any intermediate plain XML (henceforth XML). Refer to Figure 1 and "Achieving compaction with Xqueeze" below, for how this is going to be done. Similarly, the consumer will be able to parse xqML directly without conversion into intermediary XML. Thus the overhead of a compression-decompression step is eliminated. Deployments may choose to compress xqML where small file-sizes are critical.
- No loss of generality: [Updated] Unlike most other binary encoding schemes, Xqueeze does not require prior knowledge of the DTD or Schema for encoding/decoding. However, it can take advantage of the availability of these to generate more compact documents. It is true that applications like IE may not be able to display an arbitrary xqML file but plugins can be written to convert xqML to XML for display purposes.
- Easy deployment of xqML: xqML can work with the existing specifications (DTD/Schema) and it can be made to seamlessly interface with the industry standard DOM and SAX models so that applications higher up the heirarchy need not change.
Achieving Compaction with Xqueeze
Since Xqueeze is targeted at program to program interactions, the central notion is of a generator-consumer scenario. At the source end, xqML is produced from three inputs: (See Figure 1):
- Document specifications: This input is necessary for the generator to know the structure of the xqML to generate.
- Document Generation Logic: This input is necessary for the generator to know what xqML to generate. Eg. for a Radar system, the logic might continuously feed the generator with several values that the generator packs in an xqML structure and sends out. It may also be a DOM tree etc.
- xqML Generator: This piece of software is responsible for generating valid xqML out of the Document Generation logic and the Document specifications.
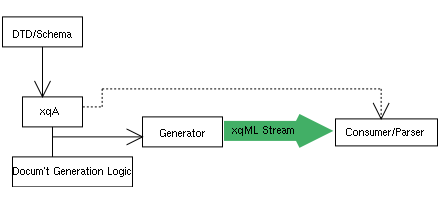
Figure 1: The xqML generation and consumption mechanism.
For generation of xqML, the generator builds a symbol-table that maps identifiers as specified in the DTD / Schema to xqML symbols using the Xqueeze algorithm. The algorithm should be such that any generator that uses it should generate the same symbol-table for the identical DTDs / Schemas. The symbol-table is known as an Xqueeze Association or xqA.
At the beginning of the run, the generator attaches the xqML version number and the xqA declaration as in plain XML files. At the receiving end, when the consumer sees the xqML indicator, it switches the parsing mode to xqML and parses the file according to it's locally generated symbol-table (which must be same as that of the generator, see previous paragraph).
In some deployments, a compression-decompression phase may be employed between the generator and consumer, as is the case with existing usage of such tools
© 2002 - 2004 Xqueeze Developers All content on this page released under OPL. This page last modified on (none).
